
How you do test for protein in a sample?
- add biuret
- it will turn from blue to purple if protein is present
How do you test for starch in a sample?
- add iodine
- it will turn from yellow/orange to black if starch is present
How do you test for glucose in a sample?
- add Benedicts solution and heat it
- it will turn from blue to orange if glucose is present
What is this molecule? What is it composed of?

DNA
It is composed of nucleotides.
Describe the structure of a protein.
- composed of amino acids joined in a chain
- then folded into complicated shapes
Is this a characteristic of a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell?
- no nucleus
prokaryotic
Is this a characteristic of a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell?
- many linear chromosomes
eukaryotic
How could you distinguish between an algae and protozoan?
Algae have chloroplasts and are green.
Is this a characteristic of a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell?
- contains mitochondria, chloroplasts, ribosomes and Golgi bodies
eukaryotic
Is this a characteristic of a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell?
- very small bacteria and archaea
prokaryotic
What is the difference in function and structure of white and red blood cells?
Red blood cells - have no nucleus, biconcave shape
- function to transport oxygen
White blood cells - have a nucleus with various shapes
- function to fight infections
What is the function of platelets?
- to clot blood after a wound
What is the function of the blood plasma?
- liquid portion of the blood that suspends the cells, transports hormones, vitamins, wastes, gases, etc.
How is the surface area of the small intestine increased?
- it is very long (approx. 7 m)
- it has villi and microvilli (finger like projections) covering the inner surface
Explain how inhalation works.
- the intercostal muscles cotnract to move the ribs up and out
- diaphragm contracts and pulls down
- this makes a larger space, therefore lower pressure
- air moves in from high pressure outside to low pressure inside
What is part F on the diagram below?
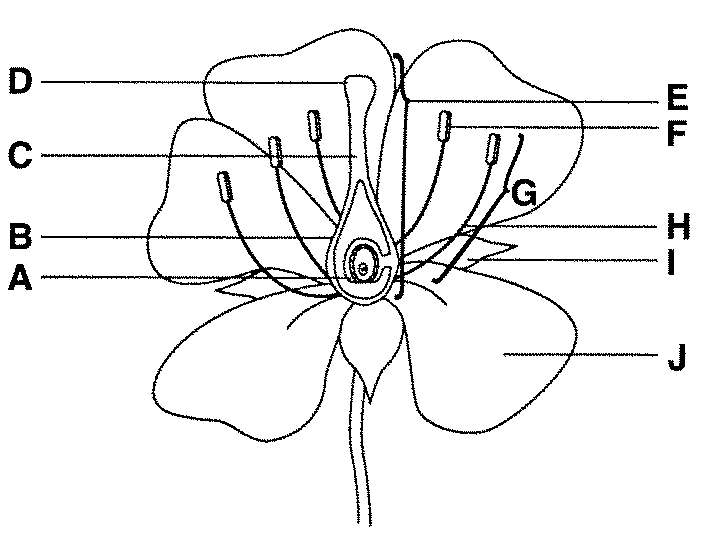
anther
What is part H on the diagram below?

filament
What is part J on the diagram below?

petal
What is part I on the diagram below?

sepal
Does it matter if you plant a seed upside down?
- no
- roots always grow down to gravity (geotropism or gravitotropism)
Which phase of meiosis is this?

anaphase 2
Which phase of meiosis is shown below?

telophase I
Which phase of meiosis is shown below?
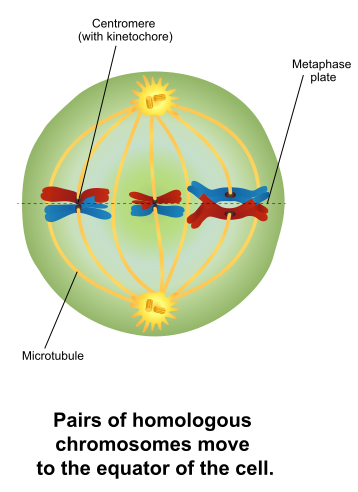
metaphase I
Brown eyes are dominant to blue eyes. A heterozygous brown eyed woman marries a heterozygous brown eyed man. Is there a possibility that they will have a blue eyed child?
B= brown eyes b= blue eyes
hetero. brown woman x hetero brown man
Bb x Bb Therefore, there is a 75% probability of brown eyed children (Bb) and a 25% probability of blue eyed children.
|
| B | b |
| B | BB | Bb |
| b | Bb | bb |
Colour-blindness is a sex-linked trait. Normal vision is dominant to colour-blindness. A colour-blind male marries a carrier female. Give the genotypes of the parents.
N = normal colour blind male x carrier female
n = colour blind XnY x XNXn